REGISTER SET OF 8085:

- 8085 have six general purpose register to store 8- bit data during execution.
- these registers are B,C,D,E,H and L.
- they can combine to perform 16-bit operation and denoted as BC,DE and HL pair.
- The accumulator is an 8-bit register .
- This register is a part of ALU unit
- This register is used to store 8-bit data and to perform arithmetic and logic operation.
- The result of an operation is stored in accumulator
- flag register are used to test data condition.
- 8085 have five flag register of 8-bit.
- these are following: Zero flag(Z), Sign flag(S), Carry flag(CY), Parity flag(P) and Auxiliary flag(AU)
Zero flag(S): If the result of arithmetic or logic operation is zero then it is set otherwise reset.
Carry flag(CY): If any arithmetic and logic operation produce any carry then carry flag is set otherwise reset.
Parity flag(P): If result of any arithmetic and logic operation contains even no of 1's then it is set otherwise reset.
Auxiliary carry flag(AU): When D3 generates any carry during arithmetic and logic operation then it is set otherwise reset.
ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT (ALU):
- It is used to perform arithmetic operation like (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) and logic operation like (AND, OR and EX-OR etc)
- It receives data from accumulator and registors.
- According to results it set or reset the flags.
PROGRAM COUNTER (PC)
- This 16-bit register deals with sequencing the execution of instructions.
- This register is a memory pointer. Memory locations have 16-bit addresses, and that is why this is a 16-bit register.
- The microprocessor uses this register to sequence the execution of the instructions.The function of the program counter is to point to the memory address from which the next byte is to be fetched. When a byte (machine code) is being fetched, the program counter is incremented by one to point to the next memory location
STACK POINTER (SP)
- The stack pointer is also a 16-bit register used as a memory pointer.
- It points to a memory location in R/W memory, called the stack.
- The beginning of the stack is defined by loading 16-bit address in the stack pointer.
INSTRUCTION REGISTER/DECODER:
Temporary store for the current instruction of a program. Latest
instruction sent here from memory prior to execution. Decoder then takes
instruction and ‘decodes’ or interprets the instruction. Decoded
instruction then passed to next stage.
Memory Address Register: Holds address, received from PC, of next program instruction. Feeds the address bus with addresses of location of the program under execution.
Control Generator: Generates signals within uP to carry out the instruction which has been
decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the uP
to be opened or closed, so that data goes where it is required, and so
that ALU operations occur.
Register Selector This block controls the use of the register stack in the example. Just a
logic circuit which switches between different registers in the set
will receive instructions from Control Unit.
General Purpose Registers uP requires extra registers for versatility. Can be used to store additional data during a program. More complex processors may have a variety of differently named registers.
Timing and Control unit:
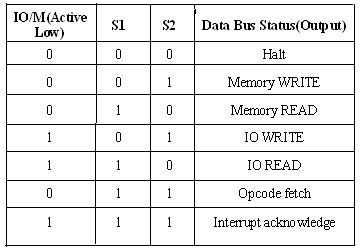
- It has three control signals ALE, RD (Active low) and WR (Active low) and three status signals IO/M(Active low), S0 and S1
- ALE is used for provide control signal to synchronize the components of microprocessor and timing for instruction to perform the operation.
- RD (Active low) and WR (Active low) are used to indicate whether the operation is reading the data from memory or writing the data into memory respectively.
- IO/M(Active low) is used to indicate whether the operation is belongs to the memory or peripherals.







ARCHITECHTURE OF 8085 MICROPROCESSOR part2